The dental industry has seen a myriad of innovations in recent years, with materials and techniques being developed to address various challenges faced by dentists and patients. One such breakthrough is the use of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) in dental applications. PMMA, a versatile and highly adaptable material, has been at the forefront of dental advancements due to its exceptional aesthetics, durability, and biocompatibility. This article delves into the benefits of PMMA in dental treatments and the future of the industry.
PMMA, commonly known as acrylic or plexiglass, has been in use for over a century, primarily as a replacement for glass. However, its unique properties have since led to its adoption in numerous other industries, including dentistry. As a dental PMMA material, it has quickly gained popularity among professionals and patients alike.
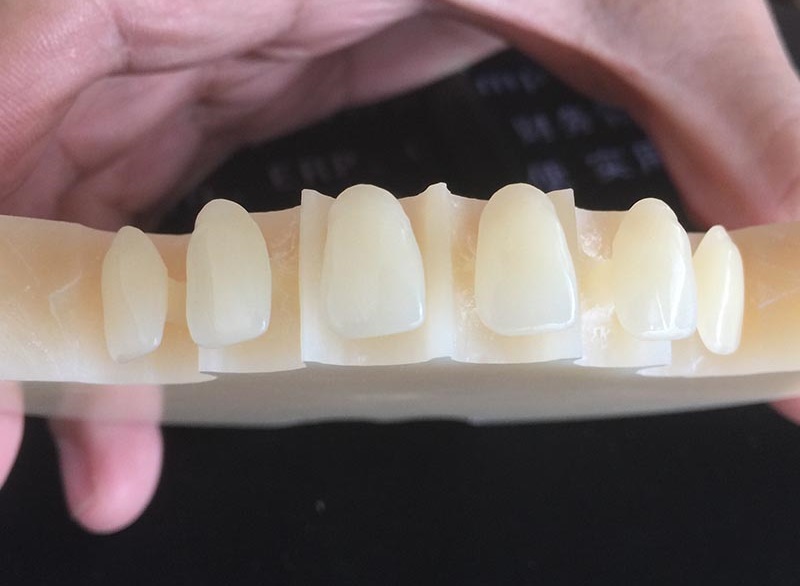
Aesthetics are crucial when it comes to dental procedures, as a confident smile can significantly impact one’s self-esteem. Traditional dental materials, like porcelain and metal, may not always provide the desired look, and that’s where PMMA shines. PMMA offers exceptional translucency and color matching, allowing for natural-looking dental restorations. Its ability to mimic the appearance of natural teeth has made it the go-to material for dentures, crowns, and bridges.
Durability is another key aspect of dental materials, as restorations need to withstand the forces of chewing and biting. PMMA’s high strength and fracture resistance ensure that it maintains its form and function for an extended period. Its low water absorption properties also contribute to its longevity, as it is less prone to distortion or bacterial infiltration.
Biocompatibility is of utmost importance in dental applications, as the materials used must not trigger any adverse reactions within the patient’s body. Dental PMMA has proven to be highly biocompatible, as it does not contain any toxic components or cause irritation to the oral tissues. This makes it an ideal material for patients with metal allergies or sensitivities.
The future of dental pmma looks promising, with ongoing research aiming to further enhance its properties. Developments in nanotechnology, for instance, are being explored to strengthen PMMA and improve its wear resistance. Moreover, digital dentistry and computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technologies are streamlining the fabrication process, leading to precise and efficient PMMA restorations.

